Hectochelle in the Halo at High Resolution:
A Stellar Spectroscopic Survey of the Galaxy
Overview
H3 is a spectroscopic survey of 325,000 high-latitude stars in the Northern hemisphere using the Hectochelle instrument on the MMT. H3 is a collaboration between the Center for Astrophysics (CfA) and the University of Arizona.
The primary goal of the H3 survey is to trace the assembly history of the Milky Way galaxy. This is acheived by measuring the 6D phase space and chemical space structure of the stellar halo. The H3 Survey is delivering radial velocities, element abundances, and spectroscopic distances, while the Gaia satellite is providing parallaxes and proper motions.
Science Goals
The H3 Survey will unravel the assembly history of the Galaxy by addressing the following key science questions:
-
Identify and characterize disrupting and disrupted dwarf galaxies in the Milky Way stellar halo using both phase space information and chemistry.
-
Measure the outer mass profile of the Galaxy and the shape of the dark matter halo.
-
Understand the transition between the thick stellar disk and the stellar halo.
Team Members
Ana Bonaca (Carnegie)
Nelson Caldwell (CfA)
Phill Cargile (CfA)
Vedant Chandra (CfA)
Charlie Conroy (CfA)
Jesse Han (CfA)
Ben Johnson (CfA)
Rohan Naidu (MIT)
Josh Speagle (U. Toronto)
Yuan-Sen Ting (OSU)
Turner Woody (CfA)
Dennis Zaritsky (U. Arizona)
Survey Design
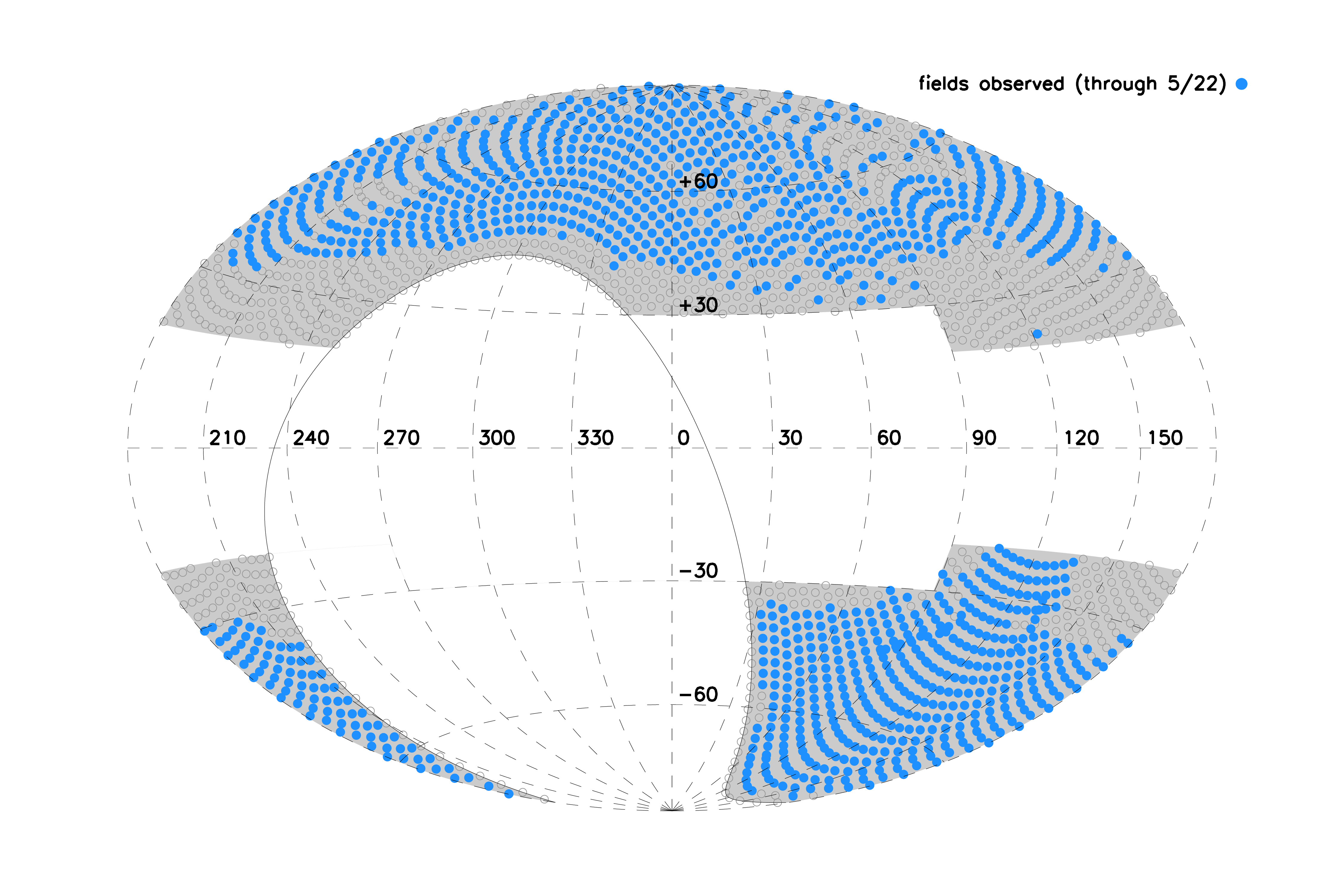
H3 stars are selected based solely on magnitude (r<18) and parallax (<0.5 mas). A sparse tiling strategy is adopted to cover 15,000 sq. degrees with 1,730 fields. These fields have been chosen to avoid the Galactic plane (|b|>20) and must be observable from Arizona (Dec.>-20).
The Hectochelle instrument provides R~32,000 spectra across the wavelength range 515nm-530nm. This interval includes the surface gravity-sensitive MgI triplet as well as numerous additional atomic transitions. The survey delivers S/N~3 at r=18, which is sufficient for high quality radial velocity measurements and, when combined with optical-NIR SED coverage, good stellar parameter estimation (temperature, surface gravity, metallicity and alpha-abundance) as well.
Publications
- Mapping the Stellar Halo with the H3 Spectroscopic Survey, Conroy et al. 2019 (link)
- Resolving the Metallicity Distribution of the Stellar Halo with the H3 Survey, Conroy et al. 2020 (link)
- A Lower Limit on the Mass of Our Galaxy from the H3 Survey , Zaritsky et al. 2020 (link)
- Timing the Early Assembly of the Milky Way with the H3 Survey, Bonaca et al. 2020 (link)
- Evidence from the H3 Survey that the Stellar Halo is Entirely Comprised of Substructure, Naidu et al. 2020 (link)
- A Diffuse Metal-Poor Component of the Sagittarius Stream Revealed by the H3 Survey, Johnson et al. 2020 (link)
- Discovery of Magellanic Stellar Debris in the H3 Survey, Zaritsky et al. 2020 (link)
- Ancient Very Metal-Poor Stars Associated With the Galactic Disk in the H3 Survey, Carter et al. 2021 (link)
- Reconstructing the Last Major Merger of the Milky Way with the H3 Survey, Naidu et al. 2021 (link)
- The Mass of the Milky Way from the H3 Survey, Shen et al. 2022 (link)
- Wide binaries from the H3 survey: the thick disk and halo have similar wide binary fractions, Hwang et al. 2022 (link)
- Live Fast, Die α-Enhanced: The Mass-Metallicity-α Relation of the Milky Way's Disrupted Dwarf Galaxies, Naidu et al. 2022 (link)
- Birth of the Galactic Disk Revealed by the H3 Survey, Conroy et al. 2022 (link)
- A Ghost in Bootes: The Least Luminous Disrupted Dwarf Galaxy, Chandra et al. 2022 (link)
- The Stellar Halo of the Galaxy is Tilted & Doubly Broken, Han et al. 2022 (link)
- Dwarf galaxy archaeology from chemical abundances and star formation histories, Johnson et al. 2023 (link)
- Distant Echoes of the Milky Way's Last Major Merger, Chandra et al. 2023 (link)
- Extending the chemical reach of the H3 survey: detailed abundances of the dwarf-galaxy stellar stream Wukong/LMS-1, Limberg et al. 2024 (link)
- All-Sky Kinematics of the Distant Halo: The Reflex Response to the LMC, Chandra et al. 2024 (link)
- Our Halo of Ice and Fire: Strong Kinematic Asymmetries in the Galactic Halo, Han et al. 2024 (link)
- Segue 2 Recently Collided with the Cetus-Palca Stream: New Opportunities to Constrain Dark Matter in an Ultra-Faint Dwarf, Foote et al. 2024 (link)
Status
325,000 spectra have been collected. The survey was completed in June 2024. Observed fields are shown in Galactic coordinates below.
The H3 Survey is funded in part by NSF award AST-2107253.